全面理解PinSage
本文为原创文章,首发地址为[全面理解PinSage - 一块小蛋糕的文章 - 知乎]
(https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/133739758)

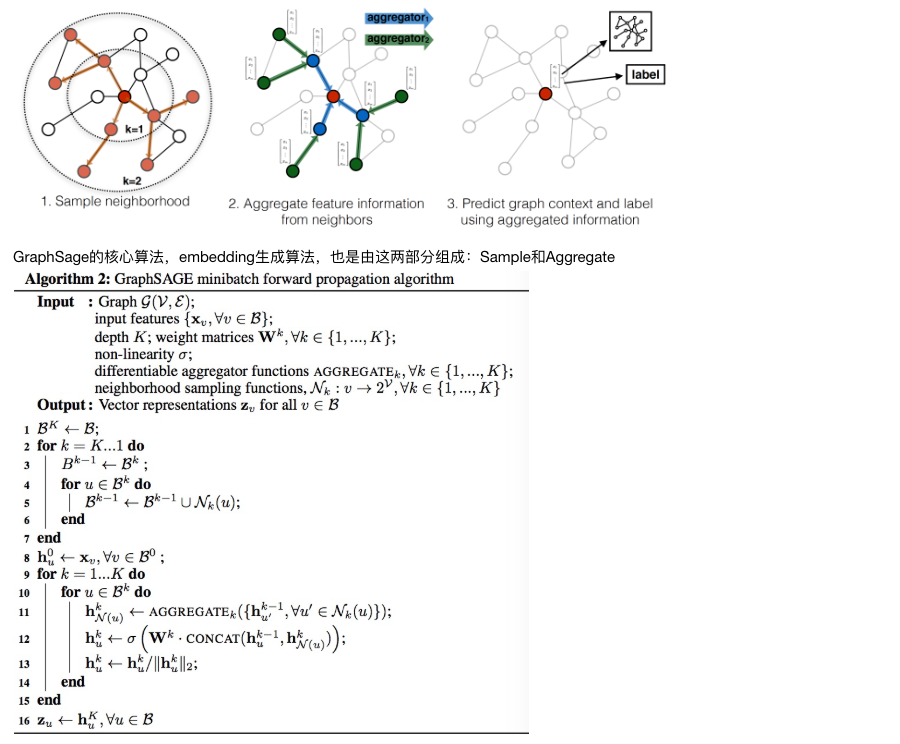





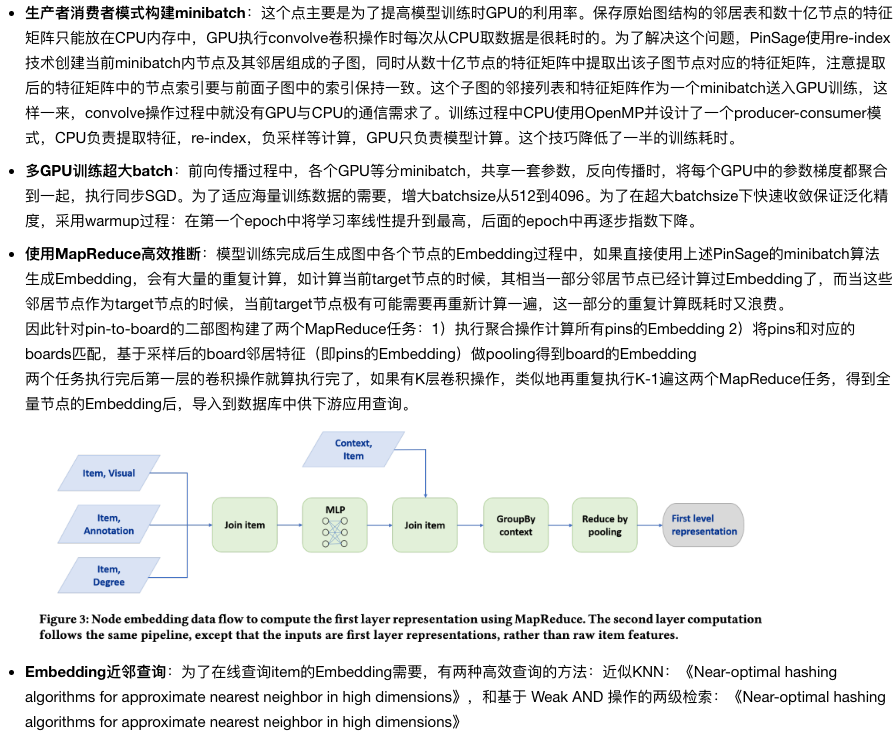

import numpy as np
import networkx as nx
import tensorflow as tf
class Convolve(tf.keras.Model):
def __init__(self, hidden_channels):
super(Convolve, self).__init__()
self.Q = tf.keras.layers.Dense(units=hidden_channels, activation=tf.keras.layers.LeakyReLU())
self.W = tf.keras.layers.Dense(units=hidden_channels, activation=tf.keras.layers.LeakyReLU())
def call(self, inputs):
# embedding.shape = (batch, node number, in_channels)
embeddings = inputs[0] # 所有节点的Embedding
# weight.shape = (node number, node number)
weights = inputs[1] # 所有边权重
# neighbor_set.shape = (node number, neighbor number) ==> (节点数,邻居数)
neighbor_set = inputs[2] # 针对每个节点采样的邻居节点id集合
# neighbor_embeddings.shape = (batch, node number, neighbor number, in channels)
# 所有邻居节点对应的Embedding
neighbor_embeddings = tf.keras.layers.Lambda(lambda x, neighbor_set: tf.transpose(tf.gather_nd(tf.transpose(x, (1, 0, 2)),
tf.expand_dims(neighbor_set, axis=-1)
),
(2, 0, 1, 3)
),
arguments={'neighbor_set': neighbor_set})(embeddings)
# neighbor_hiddens.shape = (batch, node number, neighbor number, hidden channels)
neighbor_hiddens = self.Q(neighbor_embeddings) # 所有的邻居Embedding经过第一层dense层
# indices.shape = (node number, neighbor number, 2)
node_nums = tf.keras.layers.Lambda(lambda x: tf.tile(tf.expand_dims(tf.range(tf.shape(x)[0]), axis=1),
(1, tf.shape(x)[1])))(neighbor_set)
indices = tf.keras.layers.Lambda(lambda x: tf.stack(x, axis=-1))([node_nums, neighbor_set]) # 所有邻居节点及其对应的目标节点id
# neighbor weights.shape = (node number, neighbor number)
neighbor_weights = tf.keras.layers.Lambda(lambda x, indices: tf.gather_nd(x, indices),
arguments={"indices": indices})(weights) # 提取所有要计算的邻居边的权重
# neighbor weights.shape = (1, node number, neighbor number, 1)
neighbor_weights = tf.keras.layers.Lambda(lambda x: tf.expand_dims(tf.expand_dims(x, 0), -1))(neighbor_weights)
# weighted_sum_hidden.shape = (batch, node number, hidden channels) # 对所有节点的邻居节点Embedding,根据其与目标节点的边的权重计算加权和
weighted_sum_hidden = tf.keras.layers.Lambda(lambda x: tf.math.reduce_sum(x[0] * x[1], axis=2) / (tf.reduce_sum(x[1], axis=2)+1e-6))([neighbor_hiddens, neighbor_weights])
# concated_hidden.shape = (batch, node number, in channels + hidden channels) # 节点的原始Embedding与每个节点的邻居加权和Embedding拼接
concated_hidden = tf.keras.layers.Concatenate(axis=-1)([embeddings, weighted_sum_hidden])
# hidden_new shape = (batch, node number, hidden_channels)
hidden_new = self.W(concated_hidden) # 拼接后的Embedding经过第二层dense层
# normalized.shape = (batch, node number, hidden_channels) # 结果Embedding规范化
normalized = tf.keras.layers.Lambda(lambda x: x / (tf.norm(x, axis=2, keep_dims=True) + 1e-6))(hidden_new)
return normalized
然后是minibatch算法,graph使用networkx中的graph表示,
class PinSage(tf.keras.Model):
def __init__(self, hidden_channels, graph=None, edge_weights=None):
# hidden_channels用于保存每次卷积convolve操作的输出
assert type(hidden_channels) is list
if graph is not None: assert type(graph) is nx.classes.graph.Graph # 原始图
if edge_weights is not None : assert type(edge_weights) is list # 边权重
super(PinSage, self).__init__()
# 创建卷积层
self.convs = list()
for i in range(len(hidden_channels)):
self.convs.append(Convolve(hidden_channels=[i]))
# 在原始图上计算PageRank权重
self.edge_weights = self.pagerank(graph) if graph is not None else edge_weights
def call(self, inputs):
# embeddings.shape = (batch, node number, in channels)
embeddings = inputs[0] # 所有节点的Embedding
# 邻居采样个数
sample_neighbor_num = inputs[1]
# 根据边的权重对邻居采样
# neighbor_set.shape = (node num, neighbor num) ==> (节点数,邻居数)
neighbor_set = tf.random.categorical(self.edge_weights, sample_neighbor_num) #针对每个节点采样的邻居集合
for conv in self.convs: #经过K层卷积
embeddings = conv([embeddings, self.edge_weights, neighbor_set])
return embeddings
def pagerank(self, graph, damp_rate=0.2):
# node id must from 0 to any nature number
node_ids = sorted([id for id in graph.nodes])
assert node_ids == list(range(len(node_ids)))
# adjacent matrix
weights = np.zeros((len(graph.nodes), len(graph.nodes), ), dtype=np.float32)
for f in graph.nodes:
for t in list(graph.adj[f]):
weights[f, t] = 1
weights = tf.constant(weights)
# normalize adjacent matrix line by line
line_sum = tf.math.reduce_sum(weights, axis=1, keep_dims=True)+1e-6
normalized = weights / line_sum
# dampping vector
dampping = tf.ones((len(graph.nodes), ), dtype=tf.float32)
dampping = dampping / tf.constant(len(graph.nodes), dtype=tf.float32)
dampping = tf.expand_dims(dampping, 0) # line vector
# learning pagerank
v = dampping
while True:
v_updated = (1-damp_rate) * tf.linalg.matmul(v, normalized) + damp_rate * dampping
d = tf.norm(v_updated - v)
if tf.equal(tf.less(d, 1e-4), True): break
v = v_updated
# edge weight is pagerank
weights = weights * tf.tile(v, (tf.shape(weights)[0], 1))
line_sum = tf.reduce_sum(weights, axis=1, keepdims=True) + 1e-6
normalized = weights / line_sum
return normalized